Varicocele
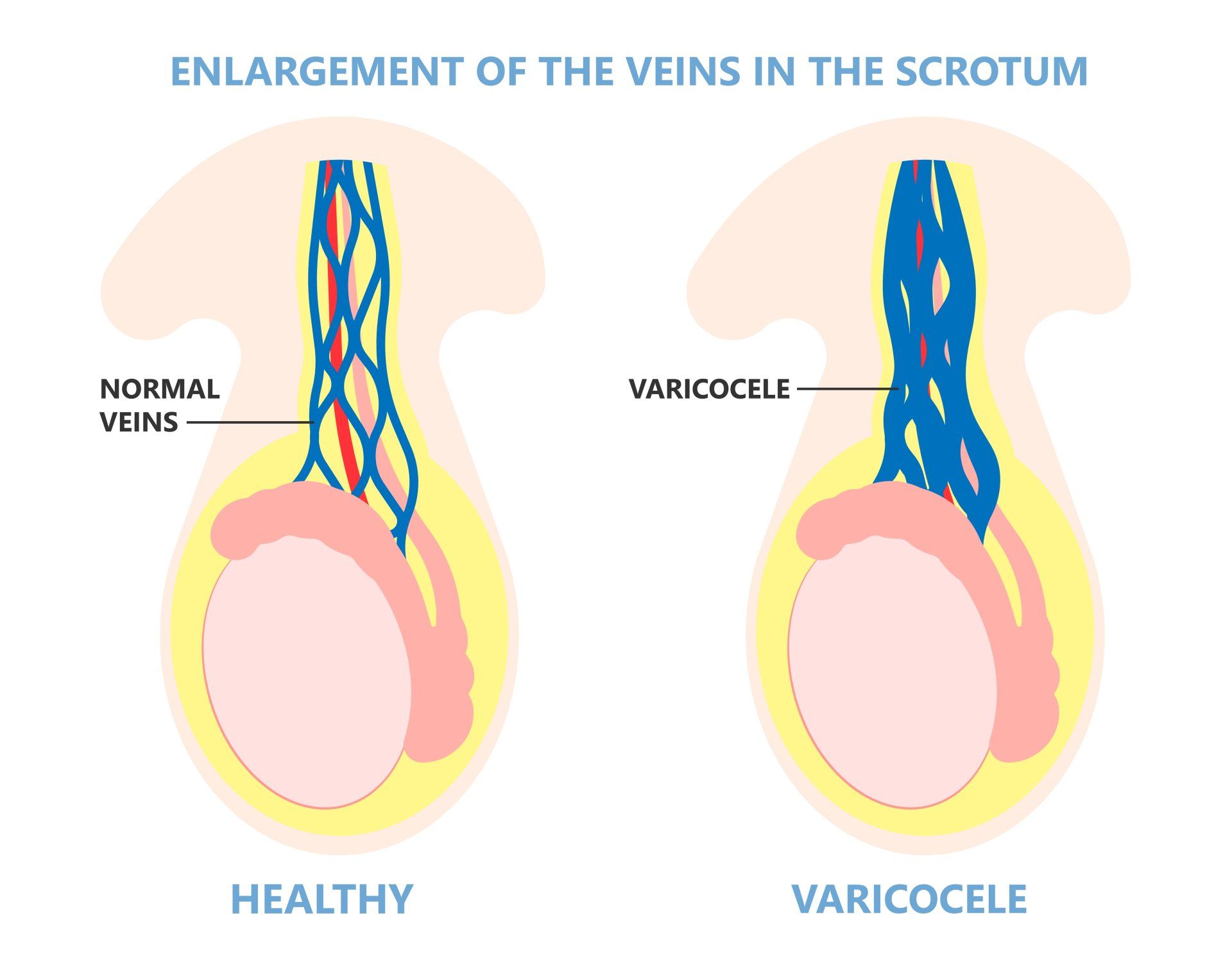
A varicocele is similar to varicose veins in the legs, but it is a dilatation of the veins of the scrotum (skin that covers the testicles).
Varicoceles usually develop after puberty and may enlarge over time. It may cause poor development of a testicle, and may lead to infertility.
Symptoms:
- May not cause symptoms at all.
- Pain: Dull, aching of the testicles worse after standing for long periods of time.
- Mass: May feel or look like a bag of worms on or just above the testicles.
- Infertility: May cause infertility.
- Left side more common than the right
Diagnosis:
Usually made on physical exam. The family physician usually sends the patient to a urologist. The urologist or family physician will then most commonly order a testicle ultrasound to diagnose the varicocele as well as make sure there is not a testicular mass or cancer. Sometimes, a CT scan may also be performed to make sure no tumors in the abdomen or pelvis that may be pressing on the veins.
Treatment:
- If asymptomatic and no problem with infertility, no need to treat.
- Minimally invasive technique performed by a vascular surgeon. The internal spermatic vein in the abdomen/pelvis that returns deoxygenated blood from the scrotum back up to the lungs to become deoxygenated. If it is not working well and not draining normally, it puts pressure on the veins in the scrotum, which then dilate resulting in a varicocele. Coil embolization of the internal spermatic vein. This is performed with intravenous sedation and lidocaine at the puncture site in the neck or groin. A catheter is then guided into the internal spermatic vein. An angiogram is performed and then coils (small metal strings that resemble springs) are placed in the vein to close it off. Once closed off, the blood reroutes and it relieves the pressure on the scrotal veins/varicocele. This should then cause the varicocele to shrink with time and improve pain and testicular function.
- Surgery is usually performed by a urologist and consists of tying off the veins. Microsurgical varicocelectomy is when an incision is made below the groin and the veins are tied off. Laparoscopic varicocele treatment is when small incisions are made in the abdomen and the veins in the pelvis that drain the varicocele are tied off or clipped.